With 5 billion people using the internet, web applications without a surprise, have become critical for business operations. E-commerce platforms, enterprise solutions and cloud technology store extensive amount of data.
But here’s the problem: the digital proliferation brings with it heightened cyber attack risks. According to a report from Verizon, 26% of all data breaches involves penetration testing web applications attacks. Plus, they are the second most common attack vector.
Imagine if the sensitive data of millions of your users are leaked on the web. Sounds nightmarish, right? It can damage brand image, affect customer trust and lead to financial loss. Web app pen testing is key to preventing such incidents.
Modern Web Application Penetration Testing emerges as a modern imperative for digital security. A proactive strategy that solves this problem by discovering vulnerabilities before attackers could exploit them.
What is Web Application Penetration Testing?
Web application pentesting involves simulating a real-world cyberattack against a web application with the aim of exploiting security vulnerabilities. However, unlike the traditional vulnerability scans, automation and manual testing combine to mimic the techniques deployed by a real threat actor.
The testing assesses different components of web application such as HTML, cookies, APIs, business logic, web servers, databases etc. cut across multiple layers of infrastructure, front end and back end.
Post examination, analysis and mitigation of vulnerabilities such as XSS attacks, broken authentication, SQL injections, insecure APIs and business logic flaws are done, preventing potential data breaches.
In effect, web application pentesting does three things for your business:
- Demonstrates how vulnerabilities can be exploited
- Assess their business impact
- And recommend measures to fix them
Want to know about other types of Penetration Testing? Check our blog: Types of Penetration Testing: A Complete Overview
Importance of Web Application Penetration Testing for Your Business
Now that you know what web application penetration testing is, let’s see its importance. Web apps are connected to the internet which means a vast amount of sensitive data is stored and protected there.
That’s why cyber attackers see it as a doorway to conduct their nefarious activities. For them, web apps are quite a lucrative target. This makes web app pentesting indispensable for the safety of your business.
1. Protect Business Operations
A single exploited vulnerability can disrupt critical services, erode user confidence and result in costly downtime. WAPT ensures that web apps support, not sabotage, your continuity.
2. Secure Your Digital Expansion
From e-commerce to customer portals and APIs, every new digital service adds exposure. Penetration testing safeguards your growing infrastructure against hidden threats.
3. Avoid Financial Fallout
Breaches are expensive, averaging millions in damages, regulatory fines and recovery costs. WAPT is a preventive investment that mitigates these high-impact risks.
4. Shift-Left Security/SDLC Integration
Implementation of web application pen testing into the software development lifecycle is crucial today. It helps in detecting flaws early, drastically reducing remediation costs and strengthens long-term security posture.
5. Trust and Compliance
Standards such as GDPR, HIPAA and PCI-DSS mandate regular web application penetration testing. Continuous testing practices can boost trust among stakeholders, clients and partners.
Penetration Testing Types Done for Web Applications
Web app penetration testing secures digital assets and ensures that apps handling sensitive data remain resilient against real-world cyberattacks. It involves assessing web applications for vulnerabilities, weaknesses and misconfigurations that hackers could exploit. To achieve comprehensive coverage, multiple types of web application pentesting are performed. Each of them offer unique insights into an application’s security posture.
1. Black Box Testing
In this type of web application pentesting, testers approach the application without prior knowledge of its internal design or code. It simulates how an external attacker might probe login pages, APIs, and user inputs to find vulnerabilities such as SQL injection, authentication bypass, or insecure session handling. This helps assess how well the web application can withstand external threats.
2. White Box Testing
This web application penetration testing type provides testers full access to the source code, architecture, and system configurations. It focuses on identifying internal flaws such as insecure coding practices, improper error handling, or weak encryption. White box testing ensures that the web application’s internal logic and data flows are secure from the ground up.
There is always a debate over which pentesting to choose. Read our blog Black Box vs White Box to understand both practices and make the best decision.
3. Grey Box Testing
Grey box web app penetration testing combines both black box and white box methods. Testers have partial information – like user credentials or limited documentation – to mimic insider threats or partially informed attackers. This testing helps determine the impact of attacks launched by users with restricted access.
4. Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST)
Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) focuses on analysing a live web application in real time. This type of web application penetration testing detects vulnerabilities like cross-site scripting (XSS), SQL injection, and security misconfigurations while the application is running, closely mirroring real attack conditions.
5. Static Application Security Testing (SAST)
In contrast, SAST examines the source code or binaries without execution. This web application pentesting method helps detect flaws early in the software development lifecycle – making it ideal for developers aiming to build security into the code from the start.
When combined, these web application penetration testing types offer a holistic view of your application’s defences, ensuring every layer – from code to runtime – is tested for potential vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
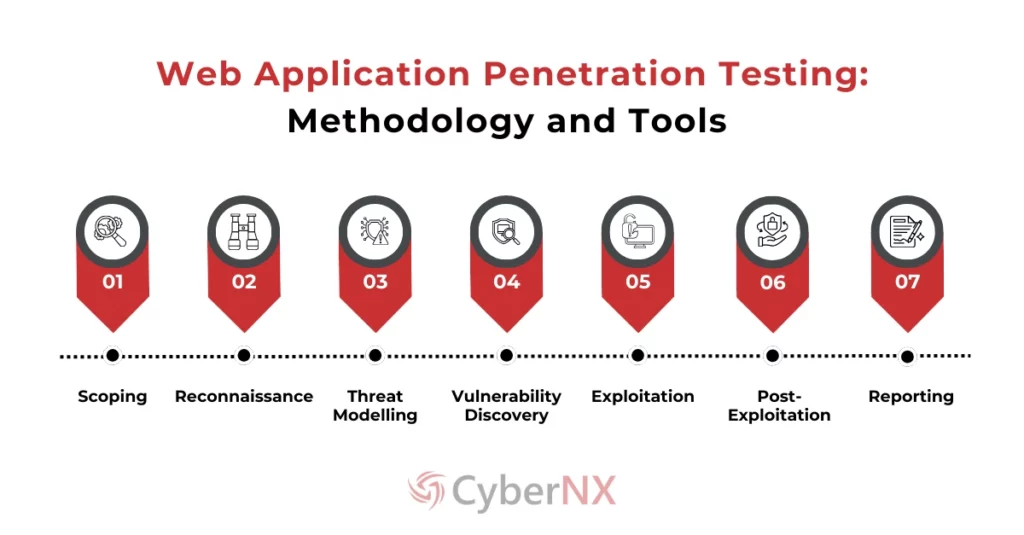
Web Application Penetration Testing: Methodology and Tools
In what is web app penetration testing section, definition might have seemed simple, but the process is daunting.
It is a very methodical, systematic and multi-phased approach. Methodologies provide the structure and discipline required to deliver actionable, consistent results. The two most referenced frameworks are:
- OWASP Web Security Testing Guide (WSTG)
- Penetration Testing Execution Standard (PTES)
Here’s a breakdown of a comprehensive methodology based on these standards and tools used in key phases:
1. Pre-Engagement and Scoping
Before penetration testing for web application begins, the objectives, rules of engagement and scope are set. It is documented clearly for pentesters and companies.
This includes:
- Identifying target environments
- Setting expectations
- Determining test types
Tools Used
No technical tools are needed in this phase.
2. Reconnaissance OR Information Gathering
Reconnaissance phase in the penetration testing for web applications is all about collecting as much data as possible about the target.
This is done without interacting directly or through limited interaction and includes discovering subdomains, services, exposed directories and web app penetration testing frameworks in use.
Some of the major techniques used include DNS enumeration, WHOIS lookups, Source code analysis and JavaScript deobfuscation
Tools Used
- Amass
- theHarvester
- Shodan
- BuiltWith
3. Threat Modelling
In this phase of penetration testing of web applications, testers study the data collected and model potential attack vectors. This helps in identifying areas where business logic, architecture or functionality are weak and can be abused.
Key Focus
Usually includes authentication and session workflows, role-based access and privilege boundaries, data flow paths and third-party and API integrations.
Tools Used
- Draw.io
- Threat Dragon
4. Vulnerability Discovery
In this phase, technical assessment begins. Using both automated scans and manual validation techniques, testers identify security flaws.
Few major ones are listed below:
- Injection points (SQL, command, XML)
- Misconfigured headers and SSL/TLS settings
- Broken access controls
- Weak authentication
Tools Used
- Burp Suite Pro
- OWASP ZAP
- Nmap
5. Exploitation
This is an essential part while doing penetration testing of web applications. Because this is where attack vectors of vulnerabilities which could be dangerous are discovered.
Once vulnerabilities are identified, critical rating of them are done. Finally, it involves safely exploiting them to understand the real-world impact.
Some of the examples include exploiting IDOR (Insecure Direct Object References) to access unauthorized data and leveraging XSS for cookie theft or phishing.
Tools Used
- Burp Suite Intruder
- SQLmap
- XSStrike
- Postman
6. Post-Exploitation
Here, pentesters evaluate the extent of access gained or compromise. Probable question like – if they could pivot to internal systems, escalate privileges, or extract large datasets? – is answered.
Activities in this phase include enumeration of internal resources, data exfiltration simulations and privilege escalation checks.
Tools:
- BloodHound
7. Reporting and Remediation Guidance
This is perhaps the most important phase for business leaders, executives and compliance managers: the web application pentest report document. It consists of the following:
- Exploited vulnerabilities
- Business impact
- Proof-of-concepts (PoCs)
- Step-by-step remediation advice
- Risk prioritization matrix
Latest Trends in Web Application Pentesting
The field of web application penetration testing is rapidly evolving to address the growing complexity of digital ecosystems and the sophistication of modern cyber threats. As businesses increasingly rely on cloud-based platforms, APIs, and third-party integrations, web application pentesting has become more advanced, data-driven, and continuous. Several emerging trends are reshaping how organizations test, secure, and monitor their web applications.
1. AI-Powered Web Application Pentesting
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming web application penetration testing by enabling automated vulnerability discovery, predictive analytics, and intelligent attack simulations. AI-based tools can scan complex codebases, detect hidden flaws, and prioritize risks faster than traditional testing methods – making web application pentesting more efficient and precise.
2. Zero Trust Security Alignment
The integration of Zero Trust principles has influenced web application penetration testing, with testers now validating every user, device, and connection instead of relying on perimeter-based defences. This ensures that web applications adhere to least privilege access, identity verification, and secure session management – core pillars of Zero Trust architecture.
3. API-Centric Web Application Pentesting
APIs are the backbone of most modern web platforms, making API security testing an essential component of web application penetration testing. Testers assess API endpoints for authorization issues, injection flaws, and insecure data handling to prevent exploitation through exposed interfaces.
4. Software Supply Chain Testing in Web Application Pentesting
Supply chain risks have pushed web application pentesting to include deeper assessments of third-party libraries, plugins, and CI/CD pipelines. This helps identify compromised dependencies or unpatched components that may introduce vulnerabilities into applications.
5. Continuous and Automated Web Application Pentesting
The shift toward DevSecOps has driven organizations to adopt continuous web app pentesting. Automated testing tools are now integrated into development workflows to identify and fix vulnerabilities in real time, ensuring ongoing protection throughout the application lifecycle.
In essence, modern web app penetration testing is no longer a one-time exercise – it’s a continuous, AI-driven, and Zero Trust – aligned process that helps businesses safeguard their digital assets against ever-evolving threats.
Conclusion
One thing is quite clear: attacker sees your web applications as a potential target to breach the environment.
Web Application Penetration Testing offers you with a proactive, resilient and intelligence-driven approach to not just to defend but defend well.
CyberNX is a trusted web application penetration testing service provider, implementing strong testing that ensures your digital innovations are built on a strong security foundation. To know more, contact us today.
Web Application Penetration Testing FAQs
How does web application penetration testing differ from a vulnerability scan?
A vulnerability scan is largely automated and focuses on detecting known issues based on signatures and configurations. It’s a broad sweep that highlights potential weaknesses but doesn’t validate them. In contrast, a web application pentest involves both automated checks and deep manual analysis. Testers actively attempt to exploit vulnerabilities to understand their actual impact—such as accessing sensitive data, bypassing controls, or altering business logic. This makes web app penetration testing a far more comprehensive and realistic assessment of an application’s security posture.
Should APIs and third-party integrations be included in a web app penetration test?
Yes, APIs and third-party services should always be within the scope of testing. Modern web applications are built on interconnected components—REST APIs, payment gateways, analytics tools, and cloud integrations—all of which expand the attack surface. APIs, in particular, often expose sensitive operations such as user authentication, data transactions, or backend logic. A flaw in any one of these can compromise the entire application. Testing these integrations ensures end-to-end security across your application’s ecosystem.
How often should web applications undergo penetration testing in agile environments?
In agile or DevSecOps workflows, penetration testing for web application should align with your release cycles. Ideally, this means conducting a full test at least once per quarter or after significant changes—such as new features, third-party updates, or infrastructure changes. For high-risk or customer-facing applications, consider integrating lightweight, continuous testing into your CI/CD pipelines. This ensures that new code is validated against security policies without waiting for the next major audit cycle.
Can business logic flaws be detected using automated tools?
No, business logic vulnerabilities cannot be reliably detected through automation alone. These flaws arise from how an application is designed to handle user actions, transactions, and workflows. For example, exploiting a checkout process to alter pricing, bypassing approval steps, or manipulating referral schemes are issues that require contextual understanding and creative thinking. Only skilled testers, mimicking real user behaviour, can identify these high-risk scenarios that tools typically overlook.