The digital landscape is constantly shifting, with new threats emerging every day. Your cybersecurity defenses might have been strong yesterday, but are they ready for tomorrow’s challenges? Think of your cybersecurity defenses as a bridge. You’ve designed it, built it, and believe it’s strong. But how do you really know it can withstand the weight of a sudden storm, a surge of traffic, or even a deliberate attempt to weaken it?
That’s where red teaming comes in. It’s like a stress test for your digital infrastructure, pushing it to its limits to identify vulnerabilities before a real disaster strikes.
Our comprehensive guide explores the critical role of red teaming in cybersecurity, providing you with the knowledge you need to stay ahead of malicious actors.
What is Red Teaming in cybersecurity?
Organizations of all sizes face the constant risk of attacks that can cripple operations, damage reputations, and lead to significant financial losses. A reactive approach, waiting for an attack to happen, is no longer sufficient. A proactive approach to cybersecurity is essential, and that’s where red teaming comes in.
Red teaming in cybersecurity is a simulated attack against an organization’s security infrastructure. A team of highly skilled security professionals, known as red teamers, emulates real-world attackers to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the organization’s defenses.
Goals of a Red Team Assessment in Cybersecurity
he scope of red teaming assessment in cybersecurity is beyond limit. Depending on the types and size of threat businesses face, red teamers will look to infiltrate your systems. Besides, they could go further and set up investigation cells to tackle even intelligence services and malicious groups known for conducting nefarious activities. Some of the common goals set for a business include:
- Identifying vulnerabilities that traditional security assessments might miss.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of security controls and incident response procedures.
- Providing actionable recommendations for improving security posture.
- Training and preparing security teams for real-world attacks.
Types of Red Teaming in Cybersecurity
Red Teaming comes in various forms, each simulating real-world threats from different angles to test an organization’s security defenses. From external attacks to insider threats, the types of red teaming reveal hidden vulnerabilities across physical, digital, and human layers.
Digital/Technical Red Teaming
This is the most common type and focuses on vulnerabilities within an organization’s digital infrastructure. It can be further categorized:
- External Network Red Teaming: Simulates attacks originating from the internet, targeting publicly accessible systems and services. This tests the effectiveness of firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other perimeter defenses.
- Internal Network Red Teaming: Simulates attacks originating from within the organization’s network, perhaps by a compromised employee account or a malicious insider. This tests the effectiveness of internal security controls and access restrictions.
- Wireless Red Teaming: Focuses specifically on vulnerabilities in wireless networks, attempting to gain unauthorized access through Wi-Fi or other wireless technologies.
- Application Red Teaming: Targets specific applications, such as web applications, mobile apps, or APIs, to identify vulnerabilities in their code and design.
- Social Engineering: While often a component of other types of red teaming, it can also be a standalone exercise. It focuses on manipulating individuals into divulging sensitive information or performing actions that compromise security. This can involve phishing emails, phone calls, or even in-person interactions.
Physical Red Teaming
This type of red teaming focuses on gaining physical access to an organization’s facilities or systems. It can involve:
- Bypassing Physical Security Controls: Attempting to bypass security measures such as locks, alarms, and security cameras.
- Social Engineering (in a physical context): Manipulating employees or visitors to gain access to restricted areas. This might involve impersonating a delivery driver or a repair technician.
- Dumpster Diving: Searching through discarded materials for sensitive information.
- Lock Picking: Attempting to pick locks to gain access to restricted areas.
Hybrid Red Teaming
This approach combines elements of both digital and physical red teaming. For example, a red team might attempt to gain physical access to a building to then access the internal network.
Continuous Red Teaming
This isn’t a type of red teaming in the same way as the others, but rather a methodology. It involves ongoing, proactive security testing that simulates real-world attack scenarios to identify vulnerabilities in a continuous manner. This contrasts with traditional, one-time red team assessments. This type of teaming often leverages automation and specialized tools to maintain a persistent state of security assessment.
Key Considerations When Choosing a Type of Red Teaming
It’s important to remember that red teaming is not a one-size-fits-all solution. The type of red teaming that’s right for your organization will depend on your specific needs and circumstances.
- Your organization’s specific risks: What are your most critical assets, and what threats are you most concerned about?
- Your budget: Physical red team services can be more expensive than digital.
- Your industry regulations: Some industries have specific requirements for red teaming activities.
Often, a combination of different approaches can be the most effective way to strengthen your overall security posture.
Why is Red Teaming Important?
The importance of red teaming stems from the ever-evolving nature of cyber threats.
- Growing Cyber-attacks: Cyber-attacks are increasing in frequency, sophistication, and impact. Organizations must be prepared to defend against these evolving threats.
- Proactive Security: It helps organizations proactively identify and address security weaknesses before they can be exploited by malicious actors.
- Attack Prevention: By simulating real-world attacks, red teaming helps organizations understand their vulnerabilities and strengthen their defenses, reducing the likelihood of successful attacks.
How Does Red Teaming Work? (Step-by-Step Process)
The red teaming process follows a structured and strategic approach, typically involving three phases to thoroughly assess an organization’s security posture:
Planning Phase:
- Setting Objectives: Clearly defining the scope and goals of the red team assessment is crucial for aligning the engagement with the organization’s security priorities.
- Rules of Engagement: Establishing clear boundaries and guidelines ensures the red team operates within ethical and legal limits, while maintaining focus on the overall assessment objectives.
- Attack Surface Identification: The red teaming framework involves identifying the systems, networks, and applications that will be targeted during the assessment, ensuring no critical areas are overlooked.
Execution Phase:
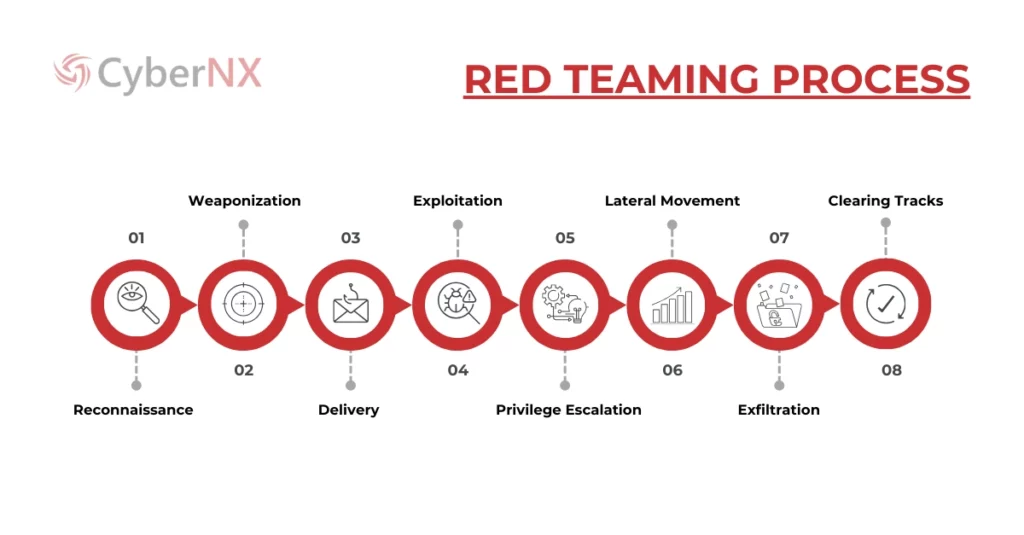
This phase involves the actual simulated attack, where red teamers deploy a variety of techniques to attempt to breach the organization’s defenses. A typical attack chain within the red teaming process involves the following steps:
- Reconnaissance: Gathering detailed information about the target organization and its systems.
- Weaponization: Developing or selecting exploits designed to target identified vulnerabilities.
- Delivery: Delivering the exploit to the target system, often through phishing emails, malicious websites, or other methods.
- Exploitation: Gaining unauthorized access to the target system by leveraging identified vulnerabilities.
- Privilege Escalation: Elevating privileges to gain deeper control over the compromised system.
- Lateral Movement: Navigating from the compromised system to other systems within the network to expand the attack surface.
- Exfiltration: Stealing sensitive data to understand the potential impact of a breach.
- Clearing Tracks: Removing evidence of the attack to ensure the simulated attack mimics a real-world adversary.
Post-Engagement Phase:
- Vulnerability Reporting: Documenting all identified vulnerabilities and weaknesses found during the simulated attack is a key step in the red teaming framework.
- Remediation Recommendations: Providing actionable recommendations for addressing the identified vulnerabilities, ensuring organizations can take proactive steps.
- Collaboration with Blue Teams: Working closely with the organization’s internal security team (blue team) to share findings and improve the overall security posture, reinforcing the organization’s defenses against future threats.
This process ensures a thorough, realistic assessment of an organization’s defenses, helping to identify weaknesses and improve overall security resilience.
Challenges in Red Teaming
Red Teaming faces challenges like evading detection, simulating realistic threats, and maintaining ethical boundaries during operations. Balancing stealth with measurable outcomes while coordinating with Blue Teams adds complexity to every engagement.
Red teaming presents several challenges:
- Ethical and Legal Considerations: Red teamers must operate within ethical and legal boundaries.
- Common Roadblocks: Technical difficulties, unexpected system behavior, and limitations on access can hinder the red team’s progress.
- Balancing Security and Business Continuity: Red team activities must be carefully planned to minimize disruption to business operations.
- Lack of Awareness: Sometimes, lack of awareness within the organization about service can create obstacles.
Common Red Team Tactics
Red teams employ a variety of tactics, including:
- Social Engineering: Manipulating individuals into divulging sensitive information or performing actions that compromise security.
- Network Service Exploitation: Targeting vulnerabilities in network services and protocols.
- Physical Security Exploitation: Attempting to gain physical access to facilities or systems.
- Application Layer Exploitation: Targeting vulnerabilities in web applications and other software.
Red Teaming Tools: Must-Haves for Successful Engagements
Red teaming tools are essential for effectively conducting simulated attacks. These tools help red teamers gather information, exploit vulnerabilities, and maintain access during engagements. Popular tools include network scanners like Nmap, exploit frameworks like Metasploit, and post-exploitation tools like Meterpreter.
Reconnaissance Tools
These tools help red teamers gather information about the target organization and its systems, a crucial first step in any attack simulation.
- Network Scanners: Nmap (Network Mapper)
- Vulnerability Scanners: Nessus
- Subdomain Enumeration Tools: Amass, Subfinder, and Assetfinder
- OSINT Frameworks: Frameworks like Maltego and Recon-ng
Exploitation Tools
Once vulnerabilities are identified, exploitation tools are used to attempt to gain unauthorized access.
- Exploit Frameworks: Metasploit provides a vast library of pre-built exploits and payloads.
- Custom Scripting: Red teamers often write their own scripts (e.g., in Python or Bash)
Post-Exploitation Tools
After gaining initial access, these tools help red teamers maintain access, escalate privileges, and move laterally within the network.
- Meterpreter: A powerful payload within Metasploit that provides a command-line interface on the compromised system, allowing for various post-exploitation activities.
- PowerShell: A powerful scripting language built into Windows that can be used for various post-exploitation tasks, such as privilege escalation and lateral movement.
Social Engineering Tools
These tools facilitate social engineering attacks, which manipulate individuals into divulging sensitive information or performing actions that compromise security.
- Social-Engineer1 Toolkit (SET): A suite of tools for creating phishing emails, fake websites, and other social engineering attacks.
- Email Spoofing Tools: Tools for crafting convincing phishing emails that appear to come from legitimate sources.
Wireless Security Tools
These tools are used to assess the security of wireless networks.
- Aircrack-ng: A suite of tools for capturing and analyzing wireless network traffic, including cracking WEP and WPA-PSK passwords.
- Wireshark: A network protocol analyzer that can be used to capture and inspect wireless traffic.
Physical Security Tools
For physical red teaming engagements, these tools might be necessary.
- Lock Picks: Tools for opening locks without the key.
- Bypass Tools: Specialized tools for bypassing physical security controls, such as card readers or biometric scanners.
Command and Control (C2) Frameworks
These frameworks allow red teamers to maintain persistent access to compromised systems and control them remotely.
- Cobalt Strike: A commercial C2 framework that provides advanced features for red teaming engagements, such as team collaboration and covert communication channels.
- Empire: An open-source PowerShell-based post-exploitation framework.
Reporting and Documentation Tools
These tools help red teamers document their findings and create comprehensive reports for the client.
- Dradis: An open-source collaboration and reporting platform.
- MagicTree: A tool for visualizing and documenting attack paths.
Take a deep dive into the tools with our blog on Red Teaming Tools.
Key Benefits of Red Teaming
- Proactive Vulnerability Identification: Discover hidden weaknesses before attackers do.
- Improved Incident Response: Enhance the organization’s ability to detect and respond to attacks.
- Strengthened Security Framework: Build a more robust and resilient security posture.
Red Teaming vs. Other Security Assessments: A Comparison
Red Teaming vs Blue Teaming
When comparing red teaming vs blue teaming, the key distinction lies in their roles within an organization’s cybersecurity framework. Red teams simulate realistic attacks, using a variety of tactics to test the organization’s defenses and response strategies. Meanwhile, blue teams defend against these simulated attacks, focusing on detection, prevention, and response. Both teams play complementary roles in strengthening cybersecurity, with red teams identifying weaknesses and blue teams improving and reinforcing the defense mechanisms to withstand real-world threats.
What else differentiates them? Read our detailed blog post Red Team vs Blue Team.
Purple Teaming
Purple Teaming bridges the gap between offensive Red Team tactics and defensive Blue Team strategies, creating a collaborative environment where both sides work together in real-time. Unlike traditional Red Team assessments that focus solely on stealth and surprise, Purple Teaming emphasizes transparency, shared learning, and continuous improvement. It transforms simulated attacks into live-fire training exercises, helping organizations fine-tune their detection and response capabilities while fostering a culture of resilience and adaptability.
Related Content: Purple Team Cybersecurity: Bridging the Gap Between Attack and Defense
Red Teaming vs. Penetration Testing
While both red teaming and penetration testing involve assessing an organization’s cybersecurity defenses, they differ significantly in their approach. Red teaming vs penetration testing typically sees penetration testing focus on identifying specific vulnerabilities in systems or applications. In contrast, red teaming takes a broader approach, simulating real-world attacks and employing a range of tactics to assess the overall security posture of an organization. The goal of red teaming is not only to identify vulnerabilities but also to understand how attackers could exploit them across multiple layers of an organization’s defenses.
Explore everything there is to know about these testing practices in our blog Red Teaming vs Penetration Testing.
Ethical Hacking and Red Team Hacking
Ethical hacking, also known as white hat hacking, involves authorized security testing to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in a system. Ethical hackers are typically hired to focus on specific weaknesses in a controlled environment. On the other hand, red team hacking takes a more comprehensive, adversarial approach by simulating real-world, sophisticated cyber-attacks. Red team hackers assess an organization’s defenses across multiple attack vectors, including technical, physical, and social engineering methods.
While ethical hacking aims to identify vulnerabilities, red team hacking goes further by testing the organization’s entire security posture, including how effectively it can respond to and mitigate attacks. Both ethical hacking and red teaming work toward the same goal of improving security, but red teaming provides a more in-depth evaluation, simulating complex attacks and testing organizational resilience in real-world scenarios.
Future Trends in Red Teaming
The future of Red Teaming is evolving with AI and automation. Advanced machine learning models are now being used to simulate adaptive adversaries, automate reconnaissance and generate polymorphic attacks. Automation are streamlining repetitive tasks, allowing human Red Teamers to focus on strategy and creativity. As environments like cloud and IoT grow more complex, AI-driven Red Teaming will enable faster, scalable threat simulations. This evolution promises proactive defense posture.
We elaborate on the future of red teaming in our blogs AI Red Teaming and Red Teaming Automation. Read now!
Conclusion
Red teaming is a crucial element of any robust cybersecurity strategy. By simulating real-world attacks, organizations can proactively identify vulnerabilities, strengthen their defenses, and improve their overall security posture.
CyberNX’s Red team services offer more than just vulnerability assessments; we act as your trusted partner, working closely with you to understand your unique business risks and tailor our approach accordingly. Our holistic methodology combines deep technical expertise with a sharp focus on your specific needs. Partner with CyberNX, your trusted red teaming solutions provider, and gain the confidence you need to face today’s cyber threats.
Red Teaming Guide FAQs
Is Red Teaming and Ethical Hacking the Same Thing?
No, red teaming and ethical hacking are not the same. Ethical hacking is a broad term that involves testing systems for vulnerabilities with permission. On the other hand, is a more comprehensive approach where security experts simulate real-world attacks to test an organization’s entire defense system, including people, processes, and technology.
What are the risks of red teaming?
The risks of this service include potential disruption to business operations, accidental exposure of sensitive data, or uncovering unknown vulnerabilities. However, these risks can be minimized with proper planning, clear guidelines, and communication to ensure the test is controlled and safe.
What is the purpose of red teaming?
The purpose of red teaming is to find weaknesses in an organization’s security by simulating real-world attacks. It helps improve defenses by identifying vulnerabilities before actual attackers can exploit them.
What is continuous automated red teaming (CART)?
Continuous automated red teaming is an ongoing approach to testing an organization’s security. Unlike other types of red teaming that are one-time assessments, continuous Automated Red teaming (CART) utilize automation to regularly simulate attacks to identify vulnerabilities and improve security in real time.
How much does a red team exercise cost?
The cost of a red team exercise in cybersecurity depends on factors such as the size of your organization, the complexity of your IT infrastructure, and the scope of the assessment. Typically, it can range from a few thousand to tens of thousands of dollars, based on the specific requirements.
Is Red Teaming only for large enterprises?
No, it is not just for large enterprises. Any organization, regardless of size, can benefit from it. It helps identify security weaknesses and improve defenses, which is important for businesses of all sizes.
Is Red Teaming legal, and what compliance frameworks apply?
Yes, it is legal when conducted within agreed boundaries. It follows a framework that ensures ethical practices and legal compliance. Common frameworks that apply include PCI DSS, HIPAA, and NIST, which often recommend red teaming to strengthen security.
How often should an organization conduct Red Teaming?
An organization should conduct red teaming at least once a year. However, high-risk industries or those with frequent system changes may benefit from more frequent assessments, such as every six months or quarterly, to maintain strong security defenses.