AI today is embedded in how organizations operate, make decisions and interact with users. But as the adoption of generative AI, LLMs and autonomous agents accelerates, so do the threats.
AI Red Teaming has thus become one of the most critical tools for evaluating the strength and security of AI systems. At the same time, AI itself has reinvented the Red Teaming exercise, enhancing every stage involved, making it effective and powerful in the hands of security professionals.
In this blog, we explore how this two-way transformation is unfolding and what it means for modern cybersecurity leaders.
What is AI Red Teaming?
There are two ways to define AI red teaming.
One is simple and straightforward: the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in red teaming stages such as reconnaissance, access and breach, exploitation and reporting. Adding AI enhances the effectiveness of each of the processes.
Another definition is the use of red teaming techniques to identifying and fixing the security holes in AI systems. This is important because AI has penetrated every business domain and thus requires rigorous testing.
How AI Is Transforming Red Teaming
Red teaming, traditionally, has relied heavily on manual techniques such as social engineering, physical intrusions, lateral movement and more. These skills remain essential.
However, AI is now capable of supercharge offensive capabilities of a security team. And there is no match to its speed, scale and adaptability.
To give you a better picture, find how AI red teaming is changing this security exercise:
1. Automated Reconnaissance
AI can scrape through the vast information available and analyse public-facing digital assets of an organization at an unprecedented pace. Parsing open-source data, spotting misconfigurations and flagging shadow IT assets is possible instantly.
2. Rapid Exploit Development
Large language models (LLMs) are now being trained on exploit databases, enabling red teams to generate attack payloads or craft phishing lures that feel uncannily legitimate and deeply customized.
This means organizations get the latest and comprehensive view of their security status against modern and advanced threats.
3. Adversarial Simulations at Scale
AI can simulate thousands of attack vectors against modern integrations such as cloud environments, APIs and AI models themselves. What once took a week can now be compressed into hours, and what took hours into minutes.
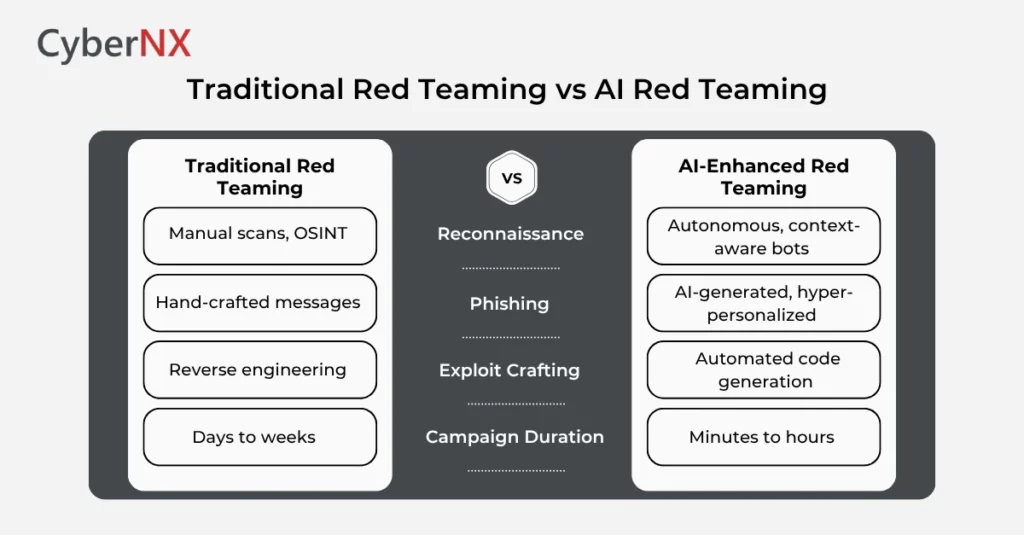
Traditional Red Teaming vs AI Red Teaming
Traditional red teaming relies on human expertise, time-intensive tactics and predefined playbooks. AI red teaming introduces automation, adaptive attacks and large-scale simulations.
However, it is important to note that human overview is still recommended with AI for best outcome.
Why Red Teaming Is Essential for AI System Security
Now it is ironic that AI systems themselves are becoming perhaps the most fragile attack surface.
Most Generative AI models are trained to be helpful, truthful and safe. But they are also shockingly susceptible to prompt injection, data extraction and manipulation attacks.
What happens when your AI customer service bot is convinced to leak internal documentation? Or when a malicious prompt causes your LLM to bypass safety filters?
Red teaming is emerging as the only effective way to stress-test these AI systems in realistic, adversarial conditions. It is just as we do for firewalls, SIEMs and endpoints.
Here are some reasons as to why this approach is necessary:
- It reveals emergent behaviour: LLMs sometimes behave in an unpredictable manner when pushed to the edge. Red teaming help uncover these behaviours early, before attackers could do.
- It simulates real-world threats: From jailbreak attempts to prompt injections and hallucination exploitation, only adversarial testing like red teaming can validate AI safety claims.
- It’s proactive, not reactive: Red teaming, which is inherently proactive, uncovers unknown threat, the most dangerous kind, protecting organizations.
Conclusion
AI red teaming is about leveraging the best of both approaches discussed to anticipate a future full of intelligent threats.
For CISOs and CTOs, it’s time to treat AI models like any other digital asset, worthy of red teaming, hardening and continuous evaluation.
The playbook is changing. The attackers are evolving. And the smartest organizations treat AI as another system that must earn trust through rigorous, adversarial validation.
Our red teaming services address advanced threats, assess existing security posture and boosts incident response capabilities by working alongside the blue team. Contact us today to know more about our red teaming expertise, experience and techniques.
AI Red Teaming FAQs
How does AI Red Teaming differ from traditional automated security testing tools?
It goes beyond vulnerability scans and static analysis. AI Red Teaming simulates intelligent, adaptive attackers that learn and evolve mid-operation. It is unlike conventional tools that follow signatures or rules. AI red teams exploit logic gaps, prompt weaknesses, and emergent behaviour in real-world conditions.
Can AI red teaming be used to test compliance with AI safety regulations?
Yes, it can proactively evaluate whether AI systems align with emerging safety, privacy, and ethical standards. It helps demonstrate due diligence by uncovering bias, data leakage, or unsafe outputs. Ultimately, it supports compliance with frameworks.
Is AI Red Teaming only relevant for large organizations or critical infrastructure?
Not at all. Any organization deploying AI models – from customer support chatbots to AI-driven fraud detection – can benefit. Even smaller companies face risks of model exploitation, and AI red teaming offers scalable, targeted validation to ensure safe deployment.
What skills or teams are needed to conduct effective AI Red Teaming?
Effective AI red teaming requires a blend of offensive security skills, prompt engineering, machine learning expertise, and ethical hacking. Some organizations build hybrid teams, while others rely on external partners who specialize in both cybersecurity and AI behaviour testing.