CBOM is quickly becoming a topic of serious interest for security leaders. Not because it is another framework to manage. But because cryptography is everywhere, and most organisations cannot clearly see it.
Encryption lives deep inside libraries, code, certificates, and configurations. Over time, this creates blind spots. Weak algorithms remain unnoticed and certificates expire silently. Quantum risk stays theoretical because no one knows what must be fixed first.
Cryptographic Bill of Materials changes that.
A CBOM gives you a structured way to discover, manage, and report cryptographic assets across applications and systems. It builds on familiar SBOM concepts, making adoption far easier than starting from scratch.
In this guide, we explain CBOM in simple terms. You will understand where it came from, how it works, and how it helps your business move towards cryptographic and quantum readiness.
Brief history of CBOM
CBOM did not appear in isolation. It emerged from a growing realisation that software supply chain security was incomplete without cryptography visibility.
SBOMs already helped organisations list software components, libraries, and dependencies. They improved vulnerability response and compliance reporting. However, they treated cryptography as an invisible internal detail.
As regulatory pressure increased and quantum computing moved closer to reality, this gap became impossible to ignore. Security teams needed to answer simple but critical questions:
- Which algorithms are we using?
- Where are weak or deprecated primitives still present?
- Which systems will break first in a post quantum world?
CBOM was introduced as an extension of the CycloneDX SBOM standard to address exactly this challenge. By reusing existing SBOM concepts and tooling, CBOM avoids reinventing the wheel while adding the depth needed for cryptographic risk management.
What is a CBOM?
CBOM stands for Cryptographic Bill of Materials. It is a specialized inventory that documents all cryptographic assets and algorithms used with the software and systems. In the era of quantum computing threats and evolving cryptographic standards, CBOM provides visibility into cryptographic posture and helps prepare for post-quantum cryptography (PQC) migration.
Key focus areas includes:
- Cryptographic Algorithms: Track RSA, ECC, AES and other algorithms used in the applications.
- Certificates & Keys: inventory TLS certificates, signing keys and encryption keys.
- Cryptographic Libraries: Identify OpenSSL, BouncyCastle and other crypto libraries.
- Quantum Vulnerability: Assess risk from quantum computing threats to current encryption.
- Protocol Usage: Document TLS versions, SSH configurations, and other crypto protocols.
- PQC Readiness: Prepare for post-quantum cryptography migration.
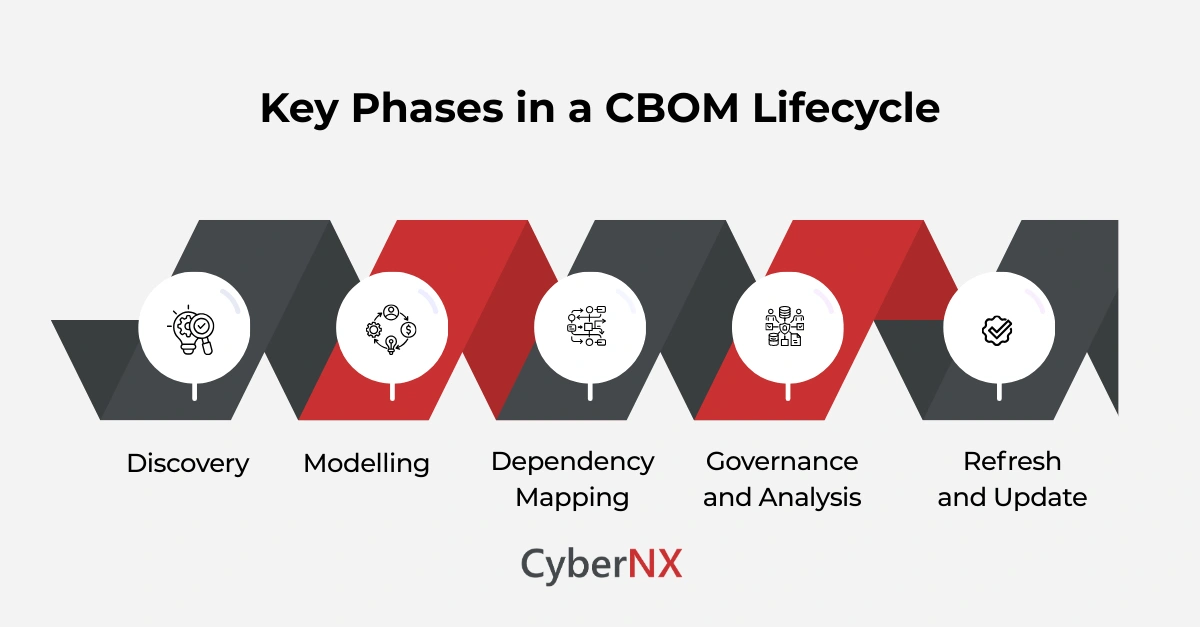
CBOM lifecycle
Here is the CBOM lifecycle you will find beginning with code scanning and ending with regenerating CBOMs.
1. Discovery
Automated tools scan applications, libraries, containers, and configurations to identify cryptographic assets such as algorithms, protocols, certificates, and keys.
2. Modelling
Each crypto asset is represented using a structured object model. Properties such as algorithm variant, mode of operation, and security level are captured.
3. Dependency mapping
CBOM distinguishes between cryptography that is:
- Implemented by a component, such as algorithms provided by a library
- Used by a component, such as algorithms actively called at runtime
4. Governance and analysis
Security teams analyse CBOMs to assess compliance, identify weak cryptography, and prioritise remediation.
5. Refresh and update
Because usage changes, CBOMs are regenerated regularly. Each CBOM reflects a snapshot in time.
CBOM formats
Cryptographic Bill of Materials is designed for practicality, not complexity. That is why it extends an existing and widely adopted standard.
CBOM builds directly on CycloneDX version 1.4. It introduces cryptographic assets as a new component type while remaining fully compatible with existing SBOM tooling. This means organisations can reuse pipelines, parsers, and governance workflows already in place.
The CBOM schema is defined as a JSON schema. It adds three core extensions:
- Component type: crypto-asset
- Properties: cryptoProperties
- Dependencies: dependencyType
Crypto assets can represent:
- Algorithms
- Certificates
- Protocols
- Related cryptographic material such as keys.
Each asset captures only the properties needed to reason about security, avoiding unnecessary noise.
An algorithm crypto asset can capture properties such as:
- Primitive: blockcipher
- Variant: AES-128-GCM
- Mode: gcm
- Certification level: fips140-3-l1
- Classical security level: 128 bits
Capturing these details enables automated reasoning and policy enforcement.
Because CBOM stays aligned with CycloneDX, adoption is smoother. Security teams do not need to choose between SBOM and CBOM. They work together.
CBOM and Indian regulatory expectations
Indian regulators are beginning to look beyond traditional software inventories and into cryptographic visibility. This shift is driven by rising supply chain risk, increased use of encryption, and long-term concerns around quantum safety.
As a result, Cryptographic Bill of Materials is moving closer to regulatory expectation, especially in sensitive and regulated sectors.
1. CERT-In Guidelines
The most direct signal comes from CERT-In, India’s national cybersecurity agency under MeitY. CERT-In has published technical guidelines that explicitly recognise CBOM and SBOM and other bills of materials.
These guidelines describe CBOM as a structured way to inventory cryptographic assets such as algorithms, certificates, protocols, and key material.
They also emphasise machine readable CBOM and SBOM formats aligned with CycloneDX and integration across the software lifecycle. While positioned as good practice, these guidelines are increasingly referenced in audits, government projects, and vendor assessments.
Financial regulators are also pushing in the same direction, even if CBOM is not yet named explicitly.
2. SEBI Guidelines
The SEBI cybersecurity and cyber resilience framework requires regulated entities to manage software supply chain risk and maintain detailed software inventories for critical systems. In practice, this creates pressure to understand embedded cryptography, certificate usage, and algorithm strength, which SBOMs alone cannot fully address.
3. RBI Guidelines
Similarly, the RBI continues to strengthen expectations around vendor risk management, cryptographic controls, and system resilience. For banks and financial institutions, being able to demonstrate where cryptography is used, how strong it is, and how it is governed is becoming essential for audit readiness.
The practical message is clear. For organisations operating in India, especially in BFSI, government, and critical infrastructure, CBOM is moving from optional best practice towards an expected security capability. Adopting CBOM early helps teams stay ahead of regulatory scrutiny while improving cryptographic governance at the same time.
Best practices for implementing CBOM
CBOM delivers the most value when applied thoughtfully.
- Start with visibility first: Even partial discovery highlights hidden cryptographic risks early.
- Prioritise usage over presence: Algorithms actively used by applications require faster remediation than unused ones.
- Standardise generation: Use consistent scanners and configurations across environments to improve data trust.
- Integrate with governance: Link CBOM outputs to cryptographic policies, audits, and risk registers.
- Track confidence levels: When probabilistic detection is used, record confidence scores to guide decisions.
Process requirements
CBOM is as much about process as technology.
1. Defined accountability
Ownership must be clear. Cryptography often sits between development, security, and infrastructure teams. CBOM governance works best when responsibilities are defined upfront.
2. Automation by default
Automation is essential. Manual cryptographic inventories do not scale. CBOM generation should integrate into CI pipelines, build processes, and runtime monitoring where possible.
3. Change management
Change management matters. Because CBOMs are snapshots, teams must define when updates occur. This could be tied to releases, configuration changes, or periodic scans.
4. Policy alignment
Policy alignment is critical. CBOM becomes powerful when mapped to cryptographic standards, internal baselines, and regulatory requirements. Without this link, it remains descriptive rather than prescriptive.
How CBOM helps your business
CBOM is not just a technical artefact. It directly supports strategic security outcomes.
- It reduces cryptographic blind spots. Teams finally gain clarity on where and how cryptography is used across complex systems.
- It strengthens compliance. CBOM simplifies audits by providing structured evidence of cryptographic controls and usage.
- It improves incident response. When vulnerabilities emerge in algorithms or protocols, CBOM helps identify affected systems faster.
- It supports quantum readiness. Migration to quantum safe cryptography starts with discovery. CBOM provides the foundation for realistic planning.
Most importantly, CBOM improves decision making. Leaders can prioritise investment based on actual cryptographic risk, not assumptions.
Conclusion
CBOM brings long overdue visibility to cryptography. By extending familiar SBOM concepts, it makes cryptographic discovery practical rather than overwhelming.
For organisations planning quantum safe transitions, improving compliance, or simply reducing hidden risk, CBOM is a natural next step. It turns cryptography from an invisible dependency into a manageable security asset.
At CyberNX, we help organisations adopt SBOM and CBOM as part of a broader cryptographic and supply chain security strategy with our advanced SBOM management tool. We work alongside your team to assess readiness, implement tooling, and translate visibility into action.
If you want clarity on your cryptographic exposure, now is the time to start the conversation.
CBOM FAQs
How is CBOM different from SBOM?
SBOM lists software components. CBOM focuses specifically on cryptographic assets and their properties, usage, and dependencies. Learn more in our blog post: CBOM vs SBOM.
Is CBOM only relevant for quantum security?
No. Quantum readiness is a major driver, but CBOM also supports compliance, vulnerability management, and cryptographic hygiene today.
Can CBOM be generated automatically?
Yes. Most CBOMs rely on automated scanning and analysis, often integrated into existing CI and security pipelines.
Does CBOM replace existing cryptographic policies?
No. CBOM supports policies by providing structured evidence and visibility. It complements governance rather than replacing it.