Vulnerability scanning is a non-negotiable component of every mature cybersecurity program. For security leaders and decision makers, it provides timely, measurable insight into where an organisation’s defences are weakest. Plus, where remediation will deliver the most business value. But how can your organization conduct vulnerability scanning that offers value specific to security, compliance and business needs? This blog explains that and much more so that you can confidently build the first line of defence.
What is Vulnerability Scanning
Vulnerability scanning is an automated review of systems, applications and cloud resources to identify known weaknesses. Scanners (there are different types available) compare asset configurations and software versions against databases of known vulnerabilities, returning a list of issues ranked by severity.
While the mechanics are technical, the outcome is straightforward. Leaders gain a continuous signal about their exposure and a repeatable method to reduce it.
A good vulnerability scanning routine is both broad and precise. Broad, because it should cover all inventoried assets. Precise, because scans need context such as asset criticality, business impact and the presence of active exploits, to be useful.
Benefits of Vulnerability Scanning
Investing in vulnerability scanning promises good business returns:
- Actionable visibility: Automated scans expose where risk concentrates, enabling prioritized investment in fixes and compensating controls.
- Cost-effective coverage: Scanning at scale is far cheaper than manual reviews and supports frequent reassessments so teams can track progress over time.
- Compliance and assurance: Regular scans demonstrate due care to auditors and regulators and can satisfy requirements for standards like PCI, ISO or relevant local rules.
- Improved resilience: Cyber attackers create exploits to break into your IT assets through gaps found. Reducing known vulnerabilities nullifies that opportunity and boosts resilience.
- Operational alignment: Scanning, when integrated into IT workflows, helps security and engineering teams by providing clear tickets and remediation guidance.
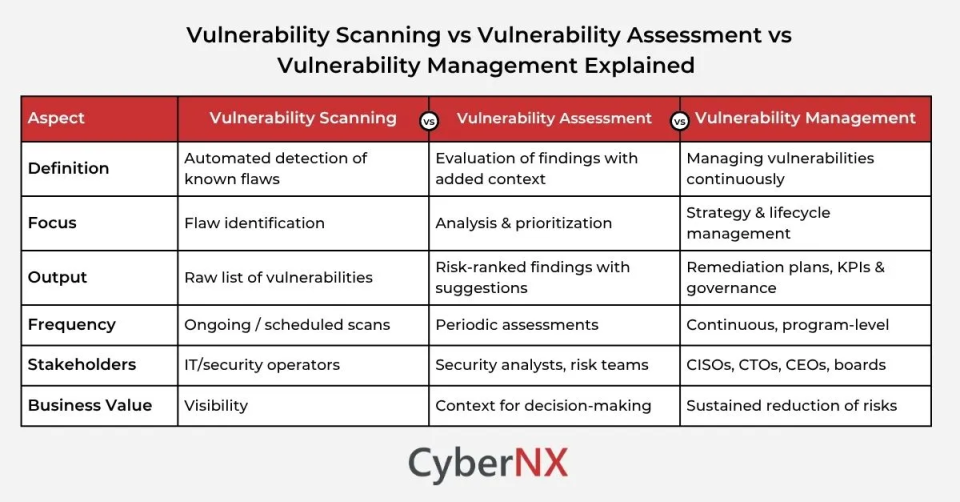
Difference Between Vulnerability Scanning, Vulnerability Assessment and Vulnerability Management
Every security professional should decode this: Vulnerability Scanning vs Vulnerability Assessment vs Vulnerability Management. Unknowingly, many can presume they are one and the same, when they clearly are not. So, what the difference?
- Vulnerability scanning: As already discussed, automation tools automate the process of finding known weaknesses in systems, networks and applications.
- Vulnerability assessment: This process is a bit more comprehensive with scoping. Plus, it includes analysing and prioritizing those findings. Often, it adds context such as business impact and exploitability of vulnerabilities found. For more insights, head over to our blog Vulnerability Assessment Guide.
- Vulnerability management: This is the broadest among the three and an ongoing program. It combines scanning and assessments with remediation, tracking, reporting and governance to systematically reduce risk. We have comprehensively covered this topic in our previous blog Vulnerability Management Guide. Read now.
For executive leaders, the distinction matters: scanning is the data source, assessment is the interpretation, and management is the strategy that ensures continuous improvement.
Here’s a chart that simplifies the differences for you:
Common Security Vulnerabilities
Understanding the typical problems that appear in scan results helps leaders translate technical lists into business actions. Common findings include:
- Missing security updates and patches for operating systems or applications.
- Insecure default configurations and exposed management interfaces.
- Weak or missing encryption and deprecated protocols.
- Open network ports and unnecessary services reachable from public networks.
- Vulnerable third-party components in application dependencies.
- Privilege and access control issues such as excessive permissions or absent multi-factor authentication.
Vulnerability Scanning Process Explained
A vulnerability scanning process uses a repeatable process tied to business risk:
- Discovery and inventory: The process starts by identifying digital assets across on-premises, cloud, containers and SaaS. This is important because incomplete inventories create blind spots.
- Risk-based scoping and cadence: Classify/categorize assets and define how often they require scanning. Now, internet-facing or public-facing systems need frequent checks than low-risk development environments.
- Tuning and detection selection: Configure scans to the environment. Use authenticated scans for deeper visibility where appropriate and targeted templates for web applications or container images.
- Validation and false-positive reduction: Every scanner produces noise. A human-in-the-loop or automated validation reduces wasted effort and preserves trust in results.
- Contextual prioritization: Combine scan findings with business context and threat intelligence so that remediation focuses on what attackers are most likely to exploit.
- Remediation workflow and verification: In this step, integrate the findings into the IT processes. Also, assign owners, track progress and re-scan to confirm closure.
- Reporting and continuous improvement: Clear, trend-based reports are given, explaining key metrics such as time-to-remediate, reduction in critical findings and coverage metrics. In addition, the program is refined based on outcomes.
Types of Vulnerability Scanning
Different scan approaches target different risk areas:
- Network scans: These review hosts, firewalls and routing equipment for exposed ports, services and known CVEs.
- Authenticated versus unauthenticated scans: Authenticated scans log in to systems to reveal additional issues that external scans cannot see; unauthenticated scans emulate an external attacker.
- Web application scans: These examine application inputs, session management and business logic for flaws such as injection risks or access control gaps.
- Cloud configuration scans: Cloud-native checks evaluate IAM policies, storage permissions, and platform-specific security settings.
- Container and image scans: These detect outdated packages and insecure build practices in container images and registries.
- Continuous scanning in CI/CD: Scanning integrated into development pipelines catches issues before release and prevents accumulation of technical debt.
Vulnerability Scanning Tools
Choose vulnerability scanning tools that match your environment and operational model. Strong platforms combine accurate detection engines, curated vulnerability intelligence, integrations with ticketing and CI/CD systems, and dashboards designed for executive consumption. Avoid tools that produce unfiltered output without remediation guidance.
When evaluating vendors, favour those that offer:
- API access for automation and orchestration.
- Authenticated checks and credential management.
- Regular intelligence feed updates and contextual scoring.
- Easy integration with your ticketing and deployment workflows.
- Clear executive reporting templates and SLAs.
Making Results Business-Ready
Raw scan output is rarely useful directly for decision-makers. Convert findings into business terms using vulnerability scanning outputs: what systems are affected, what customers or revenue streams could be impacted, and how remediation reduces measurable risk. Pair scanner outputs with asset value tagging so that a vulnerability on a production database is treated differently from the same finding on a developer test server. This translation from technical detail to business implication is the step that separates noisy security activity from true risk reduction.
Common Implementation Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Many organisations stumble in predictable ways. They run infrequent scans, treat the scanner output as the final truth, or fail to close the loop with engineering. Avoid these mistakes by setting a clear cadence, investing in validation and building remediation ownership into service-level agreements. Provide engineering teams with the tools and context they need to fix issues quickly – prioritized lists, root-cause tips, and test environments to validate patches safely.
Technology Considerations
Select tooling that supports credentialed checks, API-driven automation and clear integrations with development pipelines. Prefer platforms that can differentiate between false positives and actionable items, and that provide remediation playbooks or guidance to engineering teams. Consider vendor support for custom checks and how the solution updates its vulnerability intelligence feeds. Also evaluate operational fit: does the tool match your release cadence, and can it scale with your cloud or container growth?
Budget and Staffing
Budget for automation first: a modest investment in integrations and orchestration often reduces manual toil and speeds remediation. Complement automation with a small, skilled team for validation, triage and escalation. Cross-train engineers so they can remediate routine classes of issues without security team intervention. Finally, review budget allocations quarterly and adjust based on reduction in residual risk and the frequency of findings on critical systems.
Conclusion
Vulnerability scanning is a pragmatic, cost-effective way to reduce exposure and inform strategic cybersecurity decisions. It delivers measurable visibility, supports compliance, and accelerates remediation – provided it is implemented thoughtfully and paired with business-aware prioritization.
For executive leaders, the question isn’t whether to scan; it’s how to build a program that turns scan data into decisive action. A well-run scanning program becomes a strategic lens on risk, helping you allocate limited resources to the places that matter most. The most successful programs make security measurable and repeatable. They build scanning into the fabric of operations, use metrics to show progress and maintain a clear feedback loop between security, engineering and business leaders. Contact us today for vulnerability scanning services.
Vulnerability Scanning FAQs
What is CVSS and how should I interpret a score?
CVSS is a standardized scoring system that indicates the severity of known vulnerabilities. Scores range from low to critical; treat higher scores as candidates for faster remediation but always combine the score with asset value and exploitability before acting.
Are there legal or contractual risks when scanning third-party systems?
Yes. Scanning systems you do not own can violate terms of service or local laws. Always obtain written permission before scanning partner systems, and consult legal counsel when creating supplier security requirements.
Can scan results influence cyber insurance premiums?
Insurers increasingly review security posture, including scan histories and remediation metrics. Demonstrating consistent remediation, low residual critical exposure and integrated risk management can positively affect underwriting and premiums.
Should small organisations outsource scanning or build it in-house?
Both options are valid. Outsourcing gives quick access to expertise and tooling; in-house programs offer tighter integration with development processes. A hybrid approach – outsourced scanning and in-house remediation – often balances cost and control.