With escalating cyberattacks in the last few years, the percentage of Indian enterprises considering cybersecurity as a boardroom priority has increased. High-profile breaches, regulatory scrutiny, and increasing reliance on digital infrastructure have forced leaders to treat cybersecurity as a matter of survival.
At the heart of India’s national defence against cyber risks stands CERT-In. For many decision-makers, the term “CERT-In requirements for cybersecurity” pops up during compliance conversations or while evaluating VAPT vendors or reports, but the landscape is often shrouded in technical jargon.
What does CERT-In really do? Is it a statutory body? Does it provide certification? And more importantly, what do you as a business leader need to know to stay compliant while strengthening trust with your customers, investors and regulators
This guide takes a business-focused look at everything you need to know about CERT-In requirements for cybersecurity, cutting through the noise to show you what matters most, why it matters now, and how to act on it.
What is CERT-In? Is CERT-In a Statutory Body in India?
The full form of CERT-In is Indian Computer Emergency Response Team. It is the national body (national nodal agency) under Section 70B of the IT Act, 2000, responsible for improving India’s cybersecurity. It operates under the Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY). Since 2004, it has coordinated incident response, issued advisories, and advanced cyber readiness across public and private sectors.
Also, CERT-In is a statutory body under the Information Technology (Amendment) Act, 2008. That status gives it legal teeth: the authority to require incident reporting, prescribe controls, and enforce guidelines. For IT security leaders, this fact turns CERT-In requirements for cybersecurity from “good practice” into must-have obligations.
What is CERT-In Certification? Who Provides It?
Here’s the nuance most organizations in India may miss: CERT-In does not certify companies directly. Instead, it empanels auditing organisations that conduct assessments. This most commonly includes Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT) against the relevant audit scopes and controls. For example, CyberNX is a CERT-In empanelled auditing firm, authorized to conduct VAPT assessments.
When a company claims “CERT-In certified,” it usually means it passed an assessment by a CERT-In empanelled auditor like CyberNX and received the corresponding compliance attestation.
What CERT-In as a Body itself Offers?
CERT-In guidelines establish a unified framework for cybersecurity audits across India’s digital infrastructure. It coordinates national incident response, empanels auditors and sets expectations for audit quality and mandates timelines (e.g., the 6-hour incident reporting window) and enforcement.
- Unified Framework: Set one clear framework for cybersecurity audits
- Risk Prevention: Identify and fix risks before they cause damage
- Professional Standards: Ensure auditors follow unbiased processes
- Standardization: Standardize audit planning, conduct, and reporting
- Publishing advisories: Guidelines that define CERT-In requirements for cybersecurity
CERT-In Requirements for Cybersecurity: The VAPT Pathway
Think of Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT) as your recurring security health check. It is central to many CERT-In requirements for cybersecurity and typically follows this process:
- Scoping: Define in-scope assets such as apps, APIs, networks, cloud accounts, OT/IoT.
- Testing: Ethical hackers emulate adversaries to uncover misconfigurations and exploitable flaws.
- Analysis & Reporting: Findings include risk-severity rankings and are mapped to applicable CERT-In requirements for cybersecurity.
- Remediation & Verification: Internal security teams often fix or patches the vulnerabilities pinpointed by auditors. Also, auditors validate if the flaws are fixed.
- Attestation/Certificate: The empanelled auditor issues compliance documentation and issues CERT-In certification.
When done well, VAPT becomes the engine that converts CERT-In requirements for cybersecurity into real-world resilience.
Red Teaming and CERT-In
Although many think of CERT-In compliance as routine audits or VAPT reports, the 2025 Comprehensive Cyber Security Audit Policy Guidelines clearly includes Red Team Assessment as one of the defined audit domains. This reflects a pivotal shift. CERT-In recognizes the value of simulating real-world adversary behaviour to assess how well an organization’s entire cyber ecosystem of people, processes, and technology can withstand a coordinated attack.
This inclusion underscores that CERT-In requirements for cybersecurity are no longer limited to checklist-style testing. By embedding Red Teaming the audit lifecycle, they are encouraging organizations to validate not just compliance, but actual readiness to detect, respond, and adapt under true-to-life threat conditions.
What are CERT-In Guidelines?
The Comprehensive Cyber Security Audit Policy Guidelines (2025) act as a governance blueprint. Here are the five pillars that matter most to executives:
1. Audit Scope
A broad catalogue (26+ categories) spanning network and application security through cloud, IoT/OT, AI/ML and blockchain. This breadth ensures CERT-In requirements for cybersecurity stay relevant as your tech stack evolves.
2. Principles of Auditing
Independence, objectivity, confidentiality, and professional scepticism. These principles protect the integrity of findings so you can act on them with confidence.
3. Defined Responsibilities
The responsibility of auditors includes competency, ethics, evidence-based reporting and quality control. Leadership oversight, timely remediation, truthful disclosures and proper documentation define the responsibility of an auditee. Clear lines of responsibility help focus everyone on outcomes.
4. Process Roadmap
Standardised phases include planning, engagement terms, evidence collection, testing, reporting, and follow-up. This repeatable cadence embeds CERT-In requirements for cybersecurity into your operating rhythm rather than treating audits as one-off events.
5. Accountability Mechanisms
Consequences for non-compliance range from findings escalation to regulatory action. The message is clear: treat gaps as risks to the business, not just to IT. For boards, these guidelines translate to predictability, comparability, and accountability – exactly what strong governance demands.
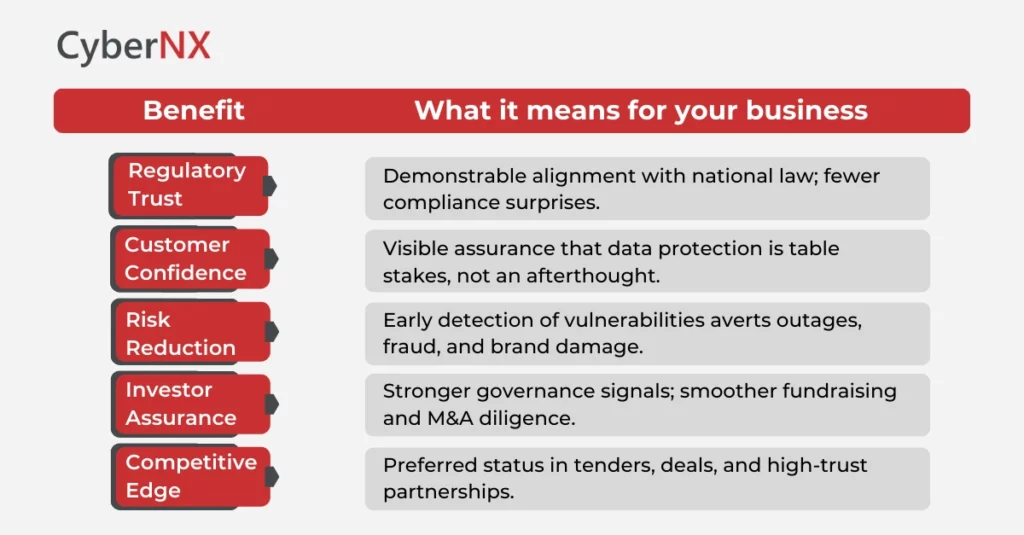
Benefits of CERT-In Certification (At a Glance)
Here are the benefits of CERT-In Certification for businesses in India:
IT leaders can use this as the trusted executive cheat sheet when conveying CERT-In requirements for cybersecurity across the C-suite.
Who Needs to Follow CERT-In Guidelines?
The coverage is wide and further widening with digital transformation sweeping organizations. You need to follow CERT-In guidelines if you are into:
| CATEGORY | EXAMPLES OF ORGANIZATIONS COVERED |
| Critical Infrastructure | Power, telecom, transport, oil & gas, defence supply chains |
| Government & Public Sector | Ministries, departments, citizen services |
| BFSI | Banks, NBFCs, payment gateways, Insurers, Fintech |
| Healthcare & Life Sciences | Hospitals, health-tech firms, research institutions handling sensitive patient data |
| Large Data Platforms | E-commerce, SaaS providers, cloud platforms, hyperscale data platforms |
| Vendors to Regulated Entities | Third-party service providers and technology partners whose clients fall under regulated industries |
Even if you are not explicitly mandated, enterprise buyers now treat CERT-In alignment as a proxy for trust. Practically, that means adopting CERT-In requirements for cybersecurity strengthens your sales posture, shortens diligence cycles and reduces procurement friction.
Audit Requirements & Frequency
According to our research, frequency is a risk decision. And our experts recommend audit at least once a year. In addition, businesses can increase frequency for critical systems, regulatory requirements, major system changes and high-risk environments.
Mandatory scenarios include hosted/third-party applications, critical systems with sensitive data, major upgrades before going live and when required by CERT-In/regulators.
Compliance & Consequences
Guidelines don’t directly penalize organizations, but:
- Contractual obligations may apply
- Regulatory compliance requirements
- Legal frameworks may impose penalties
- Reputational and business risks
How to Choose the Auditor (and Get Real Value)
First, an auditor must be CERT-In empanelled, which means authorized by CERT-In body. Other considerations include:
1. Sector Fluency
The auditor should navigate sector controls (think RBI, IRDAI, NPCI expectations) and map them cleanly to CERT-In requirements for cybersecurity.
2. Technical Depth
Beyond checklists – proven capability in VAPT for complex stacks (microservices, APIs, mobile), cloud posture (multi-account, multi-cloud), OT/IoT, and threat-led testing. Red Teaming can help with offensive security approach.
3. Transparent Methodology
Clear scoping, attack paths, evidence, and prioritised remediation guidance, not just CVSS scores.
4. Delivery Capacity
Ability to meet timelines across multiple business units without quality drift; references that vouch for execution.
5. Partnership Mindset
Also consider if the vendor they work alongside your teams through fix-verify cycles and help you institutionalise CERT-In requirements for cybersecurity (playbooks, metrics, governance).
In case you are looking for help to implement the CERT-In guidelines, here is our blog that covers what matters most: Implementing CERT-In Guidelines: Action Plan for Public and Private Enterprises in India.
The Latest CERT-In Requirements for Cybersecurity (2025 snapshot)
The 2025 update widens audit scopes to emerging tech (AI/ML systems, blockchain, IoT/OT, cloud-native architectures) and tightens auditor independence, documentation, and non-compliance consequences. The direction of travel is clear: closer alignment to real-world attack surfaces and stronger governance around assurance. Build your programme to those expectations now, not later.
Read our blog 10 Points from the Latest CERT-In Guidelines: From Audits to Threat Readiness to know more.
How CyberNX Helps?
We are a CERT-In empanelled auditor who pair human-led expertise with automation to operationalise CERT-In requirements for cybersecurity across your IT environment. We offer:
- End-to-end VAPT & Red Teaming for apps, APIs, cloud, and hybrid estates
- Remediation intelligence that prioritises fixes by business impact and attacker likelihood
- Continuous validation so your posture does not decay between audits
- Executive reporting that translates technical findings into board-ready risk narratives
- Managed Detection and Response, 24X7 SOC, Cloud Security, Compliance services
Whether you are an RBI-regulated bank, a health-tech or a SaaS platform, we help you convert compliance into customer trust and boosts security posture of your organization.
Conclusion
As cyberattacks increase exponentially, organizations should start to turn CERT-In requirements for cybersecurity into a durable advantage. IT security leaders should treat the guidelines as a governance system.
Choose CERT-In empanelled auditor who raises your security bar. Also, invest in validation between audits so controls work always and not just on audit day. Consequently, compliance becomes an outcome of strong security. That’s how you win customer trust, scale faster and stay ahead.
Contact us today to know how we can help you with cybersecurity audit to stay compliant and meet regulatory guidelines.
CERT-In Requirements for Cybersecurity FAQs
Does CERT-In recognize international cybersecurity certifications like ISO 27001 or SOC 2?
Not directly. While global frameworks such as ISO 27001 or SOC 2 complement your security posture, they don’t replace the CERT-In requirements for cybersecurity. Indian regulators expect businesses operating in critical sectors to undergo CERT-In – empanelled audits for compliance, regardless of other international certifications.
Can startups and SMEs ignore CERT-In compliance if they don’t handle sensitive data?
No. Even smaller companies may fall under CERT-In requirements if they provide technology or services to regulated industries like BFSI, telecom, or healthcare. Many SMEs are also part of supply chains where compliance obligations flow down from their larger clients.
How often do CERT-In requirements for cybersecurity change?
CERT-In updates its guidelines periodically to respond to evolving cyber threats, global best practices, and regulatory needs. For example, the 2025 policy expanded audits to cover AI, blockchain, and IoT systems. Businesses need to track these changes proactively rather than waiting for an audit deadline.
What’s the difference between a vulnerability assessment by CERT-In and a regular IT security test?
A regular IT security test may only focus on technical flaws in applications or networks. A CERT-In – mandated assessment, however, is broader – it evaluates compliance against national security standards, documentation, policies, vendor risks, and even how incidents are reported and remediated.