If you are a CISO, CEO or a founder, here’s something to ponder: Over 60% of successful cyberattacks exploit known vulnerabilities that were never patched. Yes, already known.
If that’s the case, it raises a critical question: how are these gaps missed despite regular security audits?
Spoiler alert: It is not always tools or talent but about tactics. But the manual vs automated penetration testing strategy adopted by your organization.
Choosing between the two or combining them makes a big difference. It can help you catch a threat early or suffer a costly breach. Moreover, are you testing smart or just often? The answer could be an important one for your security roadmap.
Manual Penetration Testing: Human Intelligence at Work
Manual penetration testing involves ethical hackers who simulate real-world attacks. Their aim is to identify security flaws. But unlike automated tools, which follow predefined scripts, manual testers think creatively and adaptively, mimicking sophisticated threat actors.
Advantages of manual penetration testing:
- Contextual awareness: Human testers understand business logic and assess the impact of a vulnerability based on the organization’s environment.
- Flexibility and adaptability: Manual testers can pivot strategies mid-test to follow potential attack paths.
- Discovery of complex flaws: Logical vulnerabilities, authentication bypasses, and chained exploits often go undetected by automation.
Challenges of manual penetration testing:
- Time-intensive: Deep, methodical testing takes days or even weeks.
- Higher costs: Skilled professionals command a premium for their expertise.
- Scalability limits: Manually testing expansive environments or frequent code releases is often impractical.
Despite these limitations, manual testing remains indispensable for uncovering nuanced vulnerabilities that tools simply can’t detect.
Automated Penetration Testing: All About Speed and Scale
Automated penetration testing uses specialized software to scan systems, applications and networks for known security weaknesses. It’s ideal for quickly identifying low-hanging fruit in a wide attack surface.
Advantages of automated penetration testing:
- High speed: Can scan thousands of endpoints or lines of code in minutes.
- Cost efficiency: Once configured, tools require minimal human oversight.
- Standardization: Produces consistent results with repeatable test scenarios.
Limitations of automated penetration testing:
- Miss logic-based flaws: Business logic issues or zero-days often go unnoticed.
- False positives/negatives: Results require human validation to confirm accuracy.
- Limited interpretation: Tools lack the judgment to assess severity within business context.
Automated testing is best used for routine checks and continuous monitoring, but it’s not a substitute for human insight.
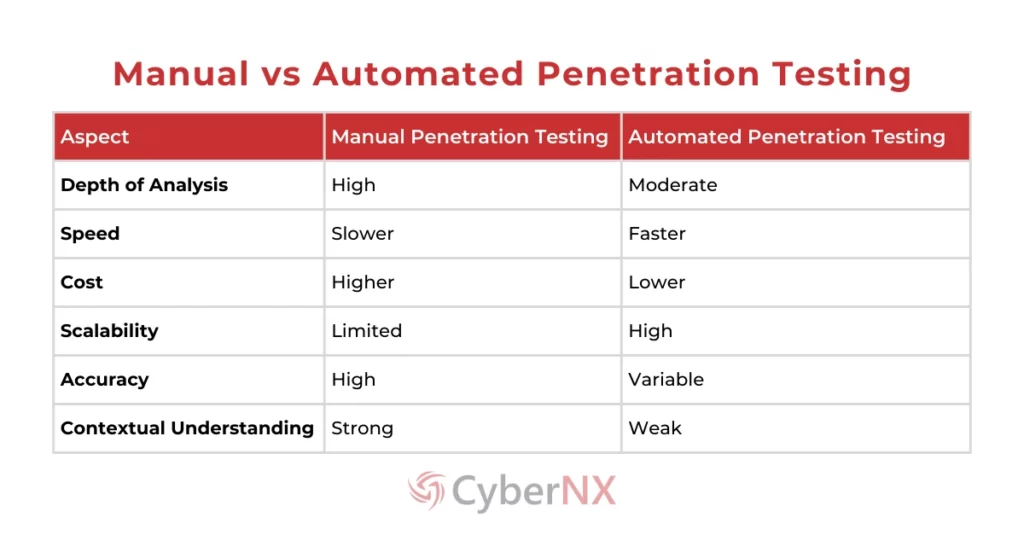
Manual vs Automated Penetration Testing: Main Differences
Manual vs automated penetration differ in execution, depth, speed and context. Manual testing relies on human expertise to uncover complex, logic-based vulnerabilities that machines often miss. In contrast, automated testing uses tools to quickly scan for known issues across large systems.
While automation offers speed and scale, manual methods bring precision and insight, making each valuable depending on your security objectives.
Manual vs Automated Penetration Testing: How About Integrating Both Approaches?
When evaluating manual vs automated penetration testing, a hybrid strategy often yields the best results. Each method addresses different needs:
Neither manual nor automated penetration testing, when used in isolation, provides complete protection against the full spectrum of cyber threats. Each has its strengths and blind spots. A hybrid approach, one that blends both methods, is essential to achieving comprehensive and actionable security coverage.
Breadth Through Automation
Automated penetration testing excels at providing broad coverage across large environments. It is well-suited for routine, scheduled scans that detect known vulnerabilities such as misconfigurations, outdated libraries, and common exposure points.
For fast-paced DevOps pipelines, automation ensures that every deployment meets a baseline security threshold without introducing unnecessary delays.
Depth Through Human Insight
Manual penetration testing, on the other hand, brings the human element necessary for understanding complex attack surfaces. Security professionals can simulate advanced adversary behaviour, chain multiple vulnerabilities, and assess the contextual and business impact of each finding.
Logic flaws, authentication weaknesses, and custom workflow exploits are areas where manual testing consistently outperforms automation.
Strategic Resource Allocation
Instead of manual vs automated penetration testing debate, a combined approach allows organizations to maximize both speed and accuracy. Automated tools handle repetitive, low-level tasks, freeing up skilled testers to focus on critical assets and high-risk scenarios.
This not only optimizes internal resources but also helps reduce alert fatigue by filtering out false positives that often accompany automated scans.
Building Resilient Security Posture
By integrating both techniques, security teams gain a layered view of their defences—broad coverage from automation and deep validation from manual testing. This balanced strategy enables better risk prioritization, improved compliance readiness, and a more agile response to emerging threats.
Ultimately, merging manual and automated penetration testing is not a compromise—it’s a strategic imperative for organizations serious about proactive, scalable, and resilient cybersecurity.
Conclusion
In the conversation around manual vs automated penetration testing, there’s no one-size-fits-all answer. Manual testing brings depth and contextual intelligence, making it invaluable for identifying high-risk issues. Automated testing delivers speed, scale, and efficiency, ideal for frequent checks.
By integrating both, security teams can strengthen their defences against both common and sophisticated threats. Making the right choice—or combination—depends on your risk appetite, infrastructure complexity, and security maturity.
If want to make decision today about manual vs automated penetration testing or a combined strategy, talk to our penetration testing experts at CyberNX.
FAQs
When should manual penetration testing be prioritized over automated testing?
Manual testing should be prioritized for high-risk systems such as payment gateways, healthcare platforms, or admin interfaces where business logic, complex workflows, or custom integrations may introduce non-obvious vulnerabilities that automation cannot detect.
Can automated penetration testing fully replace manual testing for agile development teams?
No. While automation supports rapid iteration by identifying common vulnerabilities early, it cannot assess logic flaws, chained exploits, or the real-world impact of security gaps. Manual testing remains essential for validating critical changes and performing deep assessments before major releases.
How often should organizations perform each type of testing?
Automated penetration testing should be conducted continuously or after each major change in infrastructure or code. Manual testing is best performed quarterly or biannually, and always after significant architectural changes, new application deployments, or compliance deadlines.
What’s the best way to integrate manual and automated testing into a single workflow?
Use automated tools for baseline scans integrated into CI/CD pipelines, and schedule manual testing for strategic areas and during critical development milestones. Ensure findings from both are fed into a central vulnerability management process for unified tracking and remediation.