In the contemporary digital financial ecosystem, robust cybersecurity and cyber resilience are not merely technical considerations but fundamental strategic priorities. The Securities and Exchange Board of India’s (SEBI) Cybersecurity and Cyber Resilience Framework (CSCRF) mandates regulated entities to implement comprehensive measures to safeguard operational continuity and protect investor interests. Navigating the complexities of this framework, which spans governance, technical controls, and operational processes, requires a structured and deliberate approach.
This step-by-step guide walks you through the entire journey of achieving SEBI CSCRF compliance, from gap analysis to audit readiness.
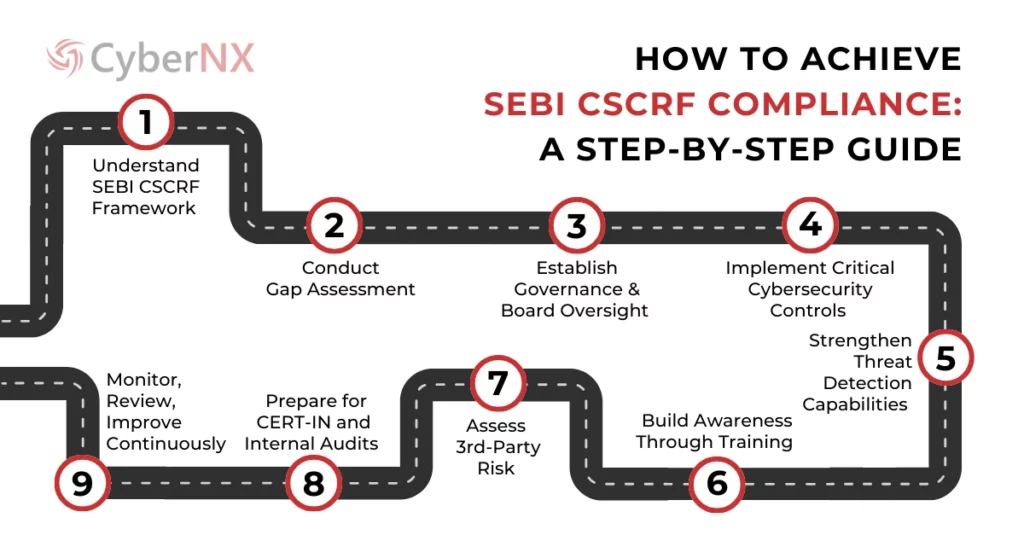
Step 1: Understand the SEBI CSCRF Framework
The CSCRF is structured around six key domains:
Governance, Identification, Protection, Detection, Response, and Recovery.
Each domain outlines specific expectations for people, processes, and technology, all aimed at reducing risk and ensuring resilience.
For a foundational understanding, read our detailed analysis on the SEBI CSCRF Overview.
Step 2: Conduct a Gap Assessment
Before making any changes, assess where your organization stands. A Gap Assessment helps identify the differential between your current cybersecurity posture and SEBI’s requirements.
Key activities include:
- Inventory Management: Developing a comprehensive inventory of extant security policies, deployed technologies, and established processes.
- Control Mapping: Formally mapping existing security controls against the specific control objectives articulated within the CSCRF.
- Risk Prioritization: Conducting a formal risk assessment and ranking of identified control gaps based on potential impact and likelihood.
Step 3: Establish Governance and Board Oversight
SEBI places significant emphasis on the integral role of board and senior management in cybersecurity oversight. Compliance necessitates:
- Committee Formation: Constituting a dedicated Cybersecurity Steering Committee or equivalent executive-level body.
- Policy Formulation: Drafting or comprehensively revising a Board-approved Cybersecurity Policy that formally articulates the organization’s commitment and strategic direction.
- Role and Responsibility Allocation: Clearly defining and formally assigning cybersecurity roles and responsibilities across relevant organizational functions.
Step 4: Implement Critical Cybersecurity Controls
Start with the most impactful controls to reduce risk:
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Network segmentation
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
- Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR)
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Step 5: Strengthen Threat Detection Capabilities
SEBI mandates proactive detection and timely response mechanisms. Strengthen capabilities through:
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Implementing and optimizing a SIEM platform for centralized log aggregation and correlation.
- Threat Intelligence Integration: Integrating relevant threat intelligence feeds to inform detection strategies and contextualize security events.
- Red Teaming Exercises: Conducting simulated attack scenarios through Red Teaming exercises to validate defensive postures and identify exploitable vulnerabilities.
- Threat Hunting Activities: Establishing proactive threat hunting capabilities to search for undetected malicious activity within the environment.
Step 6: Build Awareness Through Training
Human error is still a top cause of breaches. Your cyber awareness strategy should include:
- Employee Training: Implementing recurring training modules covering prevalent threats such as phishing, social engineering, and established incident reporting procedures.
- Role-Based Curriculum: Developing and delivering specialized training tailored to the specific cybersecurity risks and responsibilities associated with different roles (e.g., IT, Finance, HR).
- Executive Briefings: Conducting targeted cyber briefings for executive leadership and the board to ensure informed decision-making and oversight.
Step 7: Assess Third-Party Risk
Third-party vendors integrated into the operational ecosystem must adhere to comparable security standards. Implement a formal third-party risk management program:
- Vendor Inventory: Maintain an accurate and current inventory of all third-party service providers.
- Risk Classification: Classify vendors based on the criticality of services provided and the level of access granted, enabling risk-based prioritization.
- Contractual Security Clauses: Ensure robust cybersecurity clauses are incorporated into all vendor contracts, outlining security expectations and audit rights.
- Periodic Security Reviews: Conduct annual or more frequent security reviews and assessments of critical third-party vendors.
Step 8: Prepare for CERT-IN and Internal Audits
Audit readiness is not just about documentation—it’s about proving resilience.
Ensure:
- Incident response playbooks are tested
- Logs and system activity are preserved and accessible
- Policies and processes are up-to-date
Read our blog on CERT-IN Audits for SEBI CSCRF for specific requirements and best practices for audit readiness.
Step 9: Monitor, Review, and Improve Continuously
Cybersecurity is a journey. Utilize established metrics and frameworks, such as the Cyber Capability Index (CCI), to objectively measure progress, identify areas for enhancement, and inform strategic adjustments.
Final Thoughts
Achieving SEBI CSCRF compliance isn’t a one-off project—it’s a cultural shift. With a structured approach and continuous improvement, financial institutions can not only meet compliance but also build a resilient cyber defense posture.
Need expert guidance in your compliance journey? Contact CyberNX today for CSCRF advisory, red teaming, gap assessments, and managed security services.
SEBI CSCRF Compliance: Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key compliance requirements of the CSCRF?
Key requirements include:
- Establishing a Security Operations Centre (SOC) for continuous security monitoring
- Conducting Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT)
- Undergoing periodic cyber audits to verify compliance
- Implementing Incident Response Management and a Cyber Crisis Management Plan (CCMP)
- MIIs and Qualified REs must obtain ISO 27001 certification.
What is the role of the IT Committee in SEBI CSCRF Compliance?
REs (excluding Small-size and Self-certification) must have an IT Committee with at least one external cybersecurity expert. They oversee cybersecurity, review policies, monitor compliance, and advise on risk management.
What is a Cyber Capability Index (CCI) under SEBI CSCRF Compliance?
The Cyber Capablity Index (CCI) help MIIs and Qualified REs assess their cybersecurity maturity and progress. MIIs undergo third-party assessments semi-annually, while Qualified REs conduct self-assessments annually.
What is a Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) under SEBI CSCRF Compliance?
A Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) is a comprehensive list of components within a software product. It helps understand dependencies, vulnerabilities, and potential risks associated with the software.
What is the role of data classification and localization in the SEBI CSCRF Compliance?
The CSCRF emphasizes data security measures, including data classification and localization. REs must appropriately classify and protect sensitive data and comply with relevant regulations regarding data storage and transfer.